Haematology
Haematology involves the diagnosis and treatment of patients who have disorders of the blood and bone marrow. Haematology is the specialty responsible for the diagnosis and management of a wide range of benign and malignant disorders of the red and white blood cells, platelets and the coagulation system in adults and children.
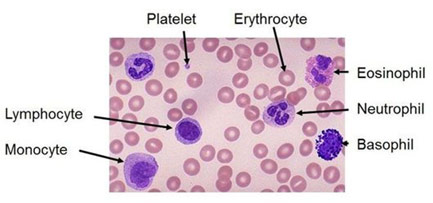
There are three categories of blood cells: red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes; white blood cells (WBCs), or leukocytes; and platelets (PLTs), or thrombocytes. Hematology is the study of these blood cells. RBC, WBC, and platelet appearance.
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) is performed on automated hematology profiling instruments and includes the RBC, WBC, and platelet measurements. Hematocrit is the ratio of the volume of packed RBCs to the volume of whole blood. RBC count, HGB, and HCT—to compute the RBC indices mean cell volume (MCV), mean cell hemoglobin(MCH), and mean cell hemoglobin concentration (MCHC).
Some examples of haematology tests are:
- Full blood count – A count of the total number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets present in blood.
- Blood film – Blood is smeared over a glass slide that is stained with specific dyes and viewed under a microscope. The number, shape and size of blood cells and the presence of any abnormal cells or immature cells are noted.
- The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) may be tested, which is the main biologic sign of inflammation.
- Iron status and anemias are assessed using tests such as serum ferritin, vitamin B12 and folate levels.
- The Coombs’ test or antiglobulin test may be used for blood typing and blood matching prior to blood transfusion, for example.
- Platelet function in bleeding and coagulation may be checked using a test called prothrombin time.
- D-dimer assessment may be performed to check for thrombotic disorders.
- Electrophoresis may be used to examine proteins in the blood such as hemoglobin and to check for hemoglobinopathies such as thalassemia or sickle cell anemia.
- The enzyme G6PD may be assessed in sickle cell disease.